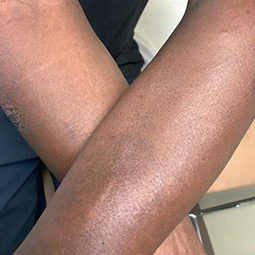
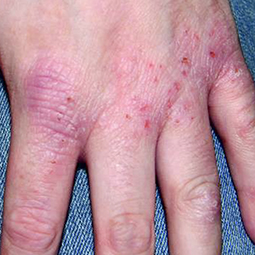
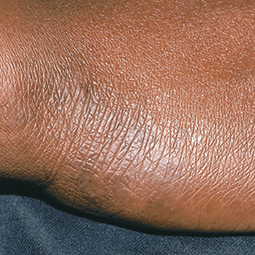
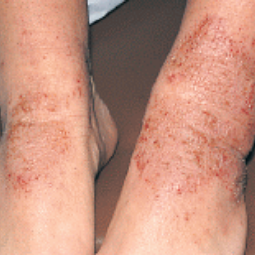
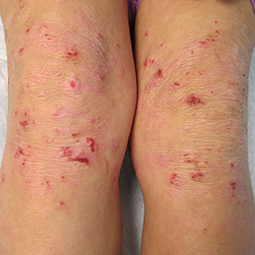
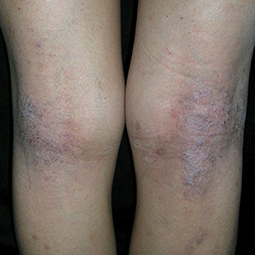
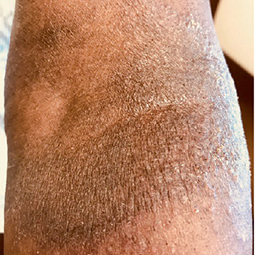
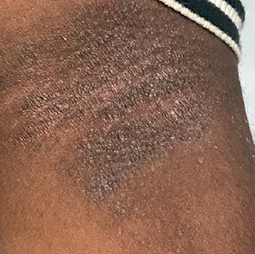
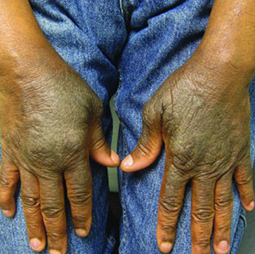
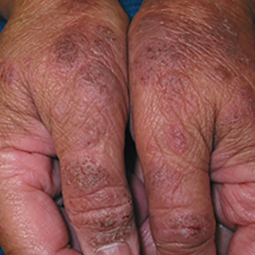
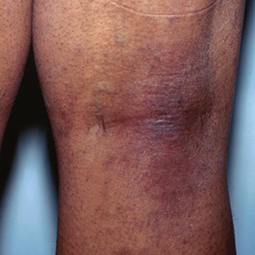
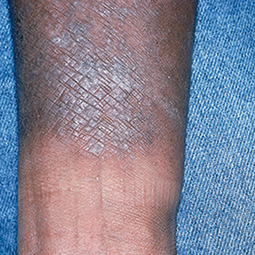
Eczema affects people of all skin colors, races, and ethnicities, with appearance varying based on skin tone and location on the body. This tool should not be used for self-diagnosis, but it can help you understand how moderate-to-severe eczema may look on different skin tones and areas of the body. Consult your doctor if you think you may have eczema.
These images feature real eczema patients who are not taking DUPIXENT and did not participate in DUPIXENT clinical trials. Moderate-to-severe eczema may look different on your skin and may appear on other areas of the body.
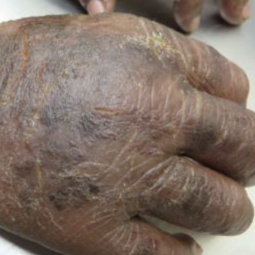
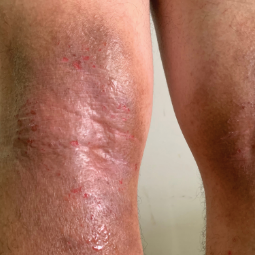
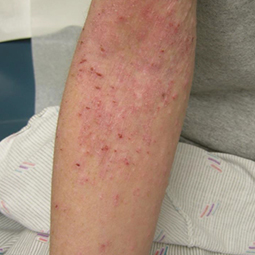
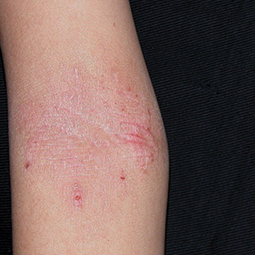
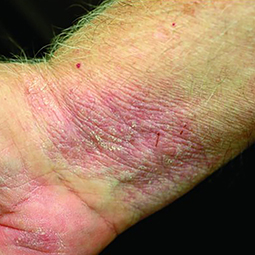
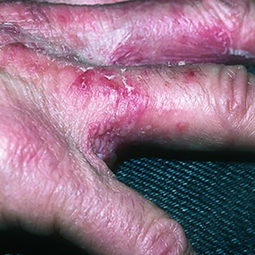
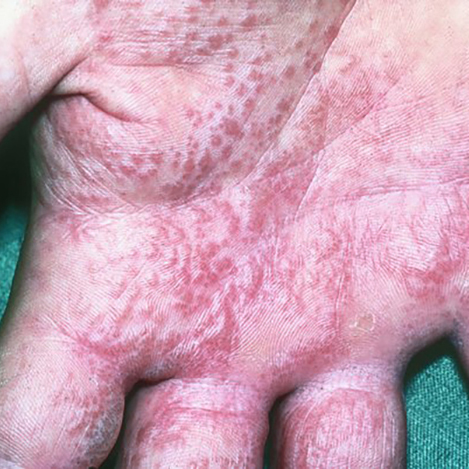
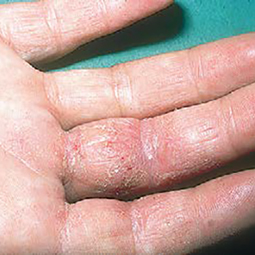
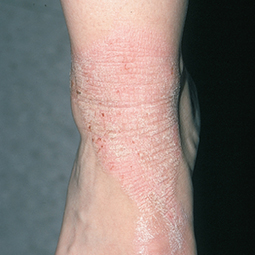
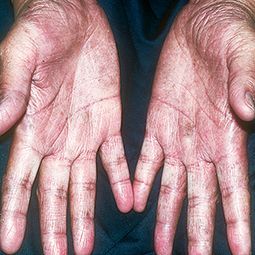
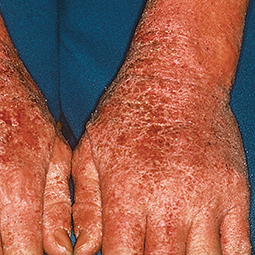
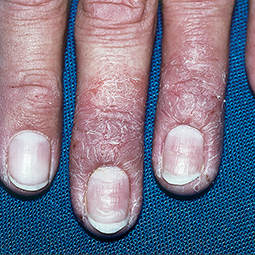
How could eczema look on my skin?
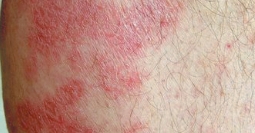
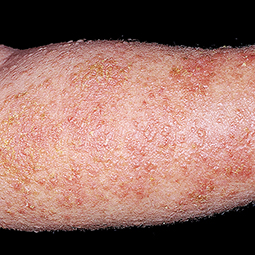
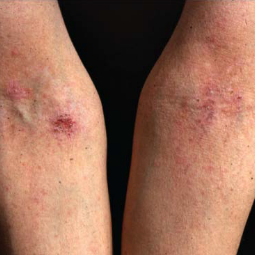
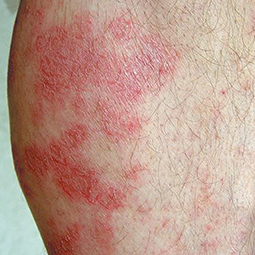
In lighter skin tones, eczema tends to appear pink or red in color.
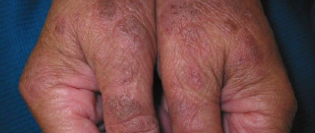
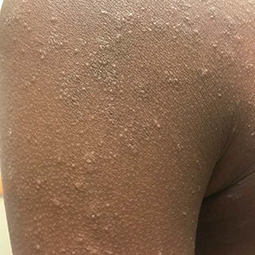
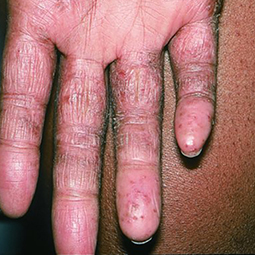
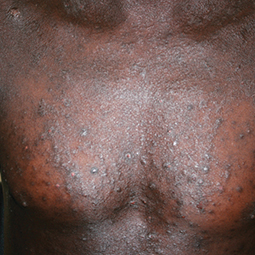
In darker skin tones, eczema tends to appear darker brown, purple, or ashen gray in color.
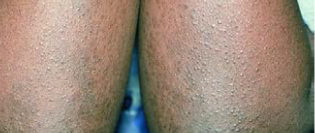
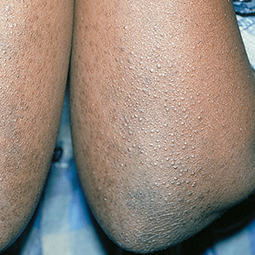
Some people with eczema may develop bumps around hair follicles that resemble goosebumps (folliculitis). These bumps can appear with or without scaly patches on the skin.
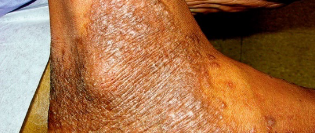
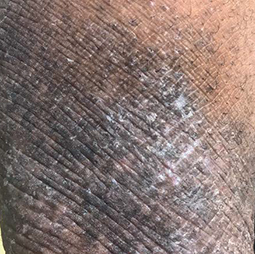
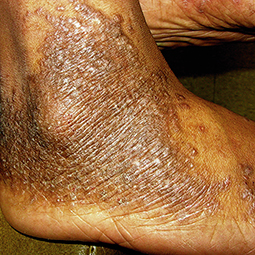
People with darker skin often experience thickening of the skin (lichenification) after flare-ups. Areas of thickened skin, or plaque, may feel rough or leathery.
Every patient is unique, so your signs and symptoms may differ from the photos above. If you suspect you may have eczema, speak to a skin specialist, who can provide a diagnosis and develop a treatment plan that works for you.
All images displayed on this page are the property of their respective copyright holders. Unauthorized use, reproduction, distribution, or
modification of these images without the express written permission of the copyright holder is strictly prohibited.
A Specialist Can Help
Eczema specialists, like dermatologists and allergists, are trained to diagnose and treat patients
of all skin tones and can help create a personalized care plan for you or your child.